

通信网络
BGP 路由过滤
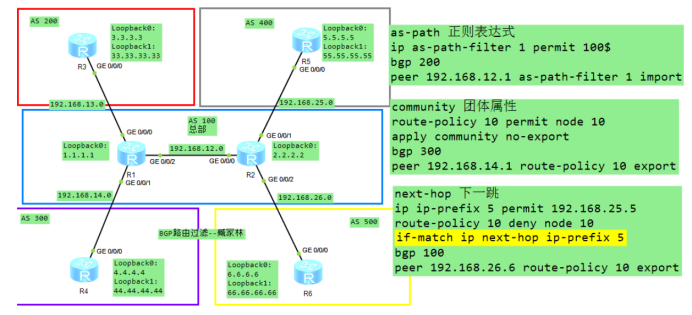
R1: bgp 100 roruter-id 1.1.1.1 peer 192.168.13.3 as-n 200 peer 192.168.14.4 as-n 300 peer 192.168.12.2 as-n 100 peer 192.168.12.2 next-hop-local net 1.1.1.0 24 R2: bgp 100 router-id 2.2.2.2 peer 192.168.25.5 as-n 400 peer 192.168.26.6 as-n 500 peer 192.168.12.1 as-n 100 peer 192.168.12.1 next-hop-local net 2.2.2.0 24 R3: bgp 200 router-id 3.3.3.3 peer 192.168.13.1 as-n 100 net 3.3.3.0 24 R4: bgp 300 router-id 4.4.4.4 peer 192.168.14.1 as-n 100 net 4.4.4.0 24 R5: bgp 400 router-id 5.5.5.5 peer 192.168.25.2 as-n 100 net 5.5.5.0 24 R6: bgp 500 router-id 6.6.6.6 peer 192.168.26.2 as-n 100 net 6.6.6.0 24
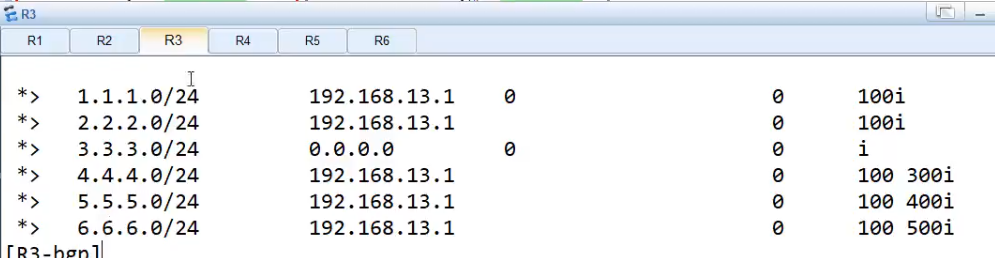
没做过滤前,dis bgp routing-table
第一个用 AS-Path进行路由过滤
利用 AS-Path 进行路由过滤
让R3只接收来自AS 100的
做正则表达式
R3:
ip as-path-filter 1 permit 100$ 匹配始发AS 100
bgp 200
peer 192.168.13.1 as-path-filter 1 import
做完过滤后再R3上, dis bgp routing-table
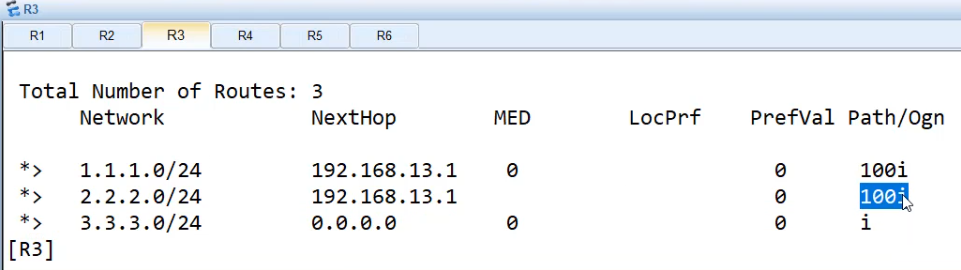
正则表达式

第二个用 Community 属性进行路由过滤
R4环回接口 4.4.4.4 只发给R1和R2,其他都收不到。community no-export
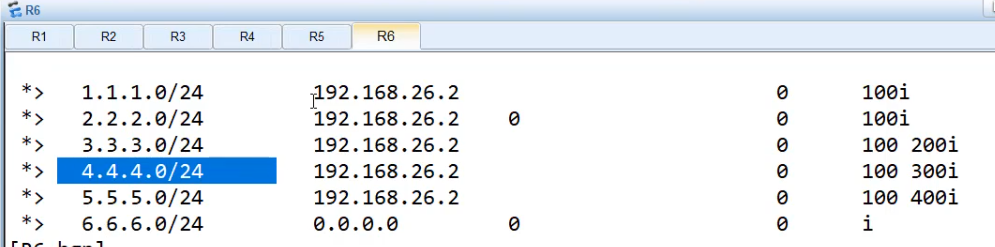
没做过滤前,先在R6查看 bgp路由表,有4.4.4.4
R1:
[R1]bgp 100
peer 192.168.12.2 advertise-community
R4:
[R4]route-policy 10 permit node 1 不写if-match,默认是所有
apply community no-export
[R4]bgp 300
peer 192.168.14.1 route-policy 10 export
peer 192.168.14.1 advertise-community 为了让这个属性值能被识别到
R1上dis bgp communtiy
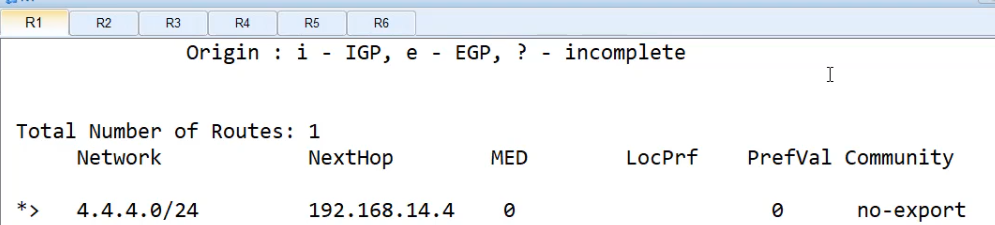
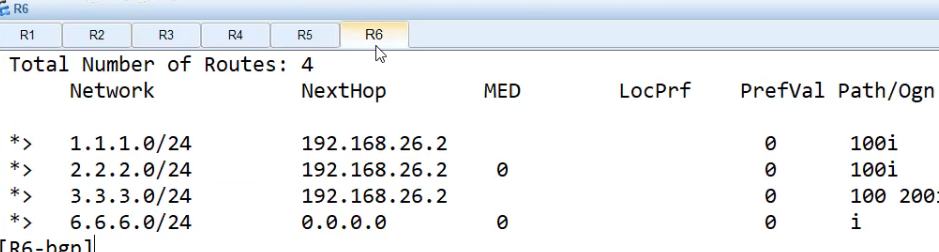
R6查看 dis bgp routing-table
第三个用 Next Hop 属性进行路由过滤
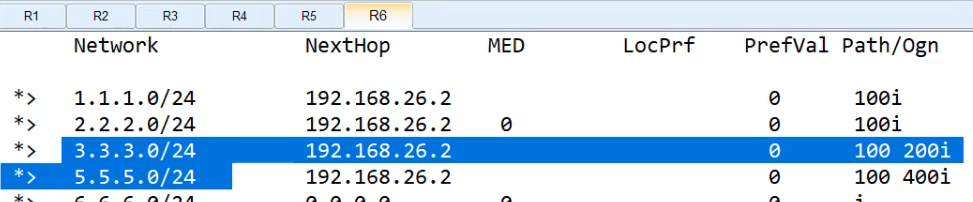
R6不接收R5发过来的路由条目
没过滤前,在R6 dis bgp routing-table
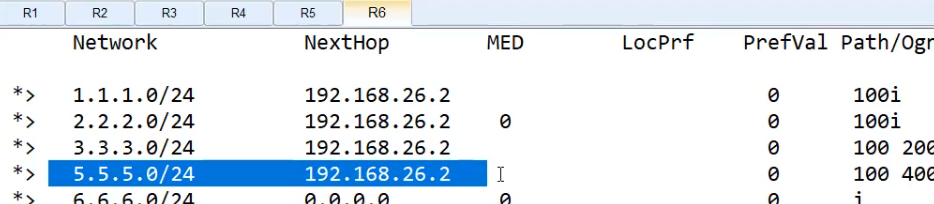
R2在发给R6的时候,把下一跳是R5的地址,做拒绝后 发送给R6
R2收到5.5.5.5的路由条目,然后发送给R6。如果想拒绝就要在R2上匹配到5.5.5.5,即下一跳是 192.168.25.5
R2:
ip ip-prefix 1 permit 192.168.25.5 32
route-policy 10 deny node 1
if-match ip next-hop ip-prefix 1
route-policy 10 permit node 2
bgp 100
peer 192.168.26.6 route-policy 10 export
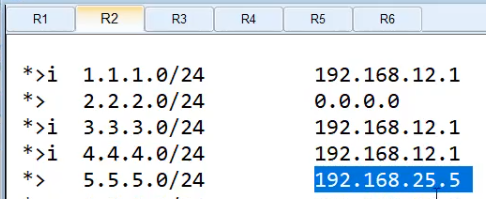
配置完成后,在R6上查看,等一会 或者直接 [R6]refresh bgp all import
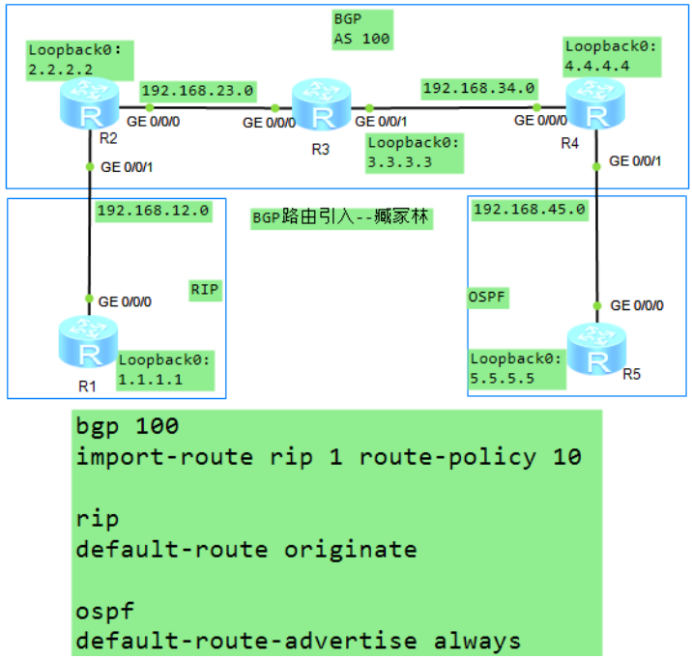
BGP 路由引入
在多协议混合的网络环境中,不同的路由协议使用的协议报文各不相同,就好比说着不同的语言。如果一种路由协议需要从别的路由协议那里获取路由信息,则可以使用路由引入技术。
希望1.1.1.1能和5.5.5.5互通
R2和R4间采用静态路由
[R2]ip route-static 192.168.34.0 24 192.168.23.3
[R4]ip route-static 192.168.23.0 24 192.168.34.3
建立BGP邻居
[R2]bgp 100
router-id 2.2.2.2
peer 192.168.23.3 as-n 100
peer 192.168.34.4 as-n 100
[R3]bgp 100
router-id 3.3.3.3
peer 192.168.23.2 as-n 100
peer 192.168.34.4 as-n 100
[R4]bgp 100
router-id 4.4.4.4
peer 192.168.34.3 as-n 100
peer 192.168.23.2 as-n 100
R2和R1运行的是RIP
[R2]rip
version 2
net 192.168.12.0
[R1]rip
version 2
net 192.168.12.0
net 1.0.0.0
R4和R5运行的是OSPF
[R4]ospf router-id 4.4.4.4
area 0
net 192.168.45.4 0.0.0.0
[R5]ospf router-id 5.5.5.5
area 0
net 192.168.45.5 0.0.0.0
net 5.5.5.5 0.0.0.0
为了能互通,rip引入bgp,ospf引入bgp,在bgp的路由上做
[R2]bgp 100
import-route rip 1
[R3]bgp 100
import-route ospf 1
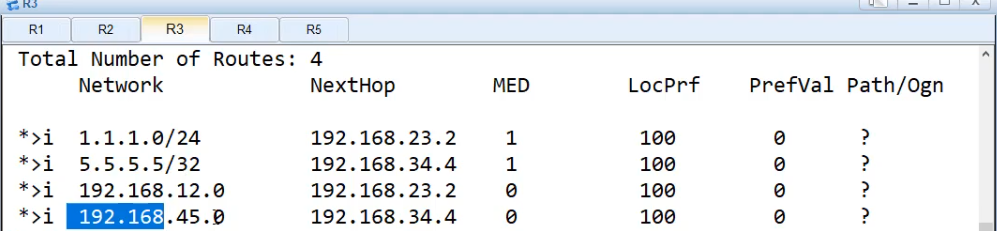
会发现除了1.1.1.1和5.5.5.5需要的外, 12和45网段的也引进来了
如果想精确引入呢?
[R2]acl 2000
rule permit source 1.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
route-policy 10 permit node 10
if-match acl 2000
[R2]bgp 100
import-route rip 1 route-policy 10
[R4]ip ip-prefix 10 permit 5.5.5.5 32
route-policy 10 permit node 1
if-match ip-prefix 10
[R4]bgp 100
import-route ospf 1 route-policy 10
[R3]dis brp routing-table
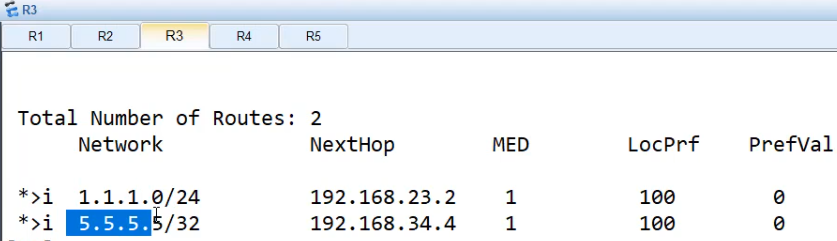
这样做好之后,R1并不能ping通R5
因为R1没有R5的路由,只做了单向引入, bgp不适合引入到rip,可以通过下放默认路由。bgp的路由条目要下放默认路由。
[R2]rip
default-route originate
[R4]ospf
default-route-advertise always
因为R4没有一个缺省路由,只能采用强制下放
BGP 缺省路由
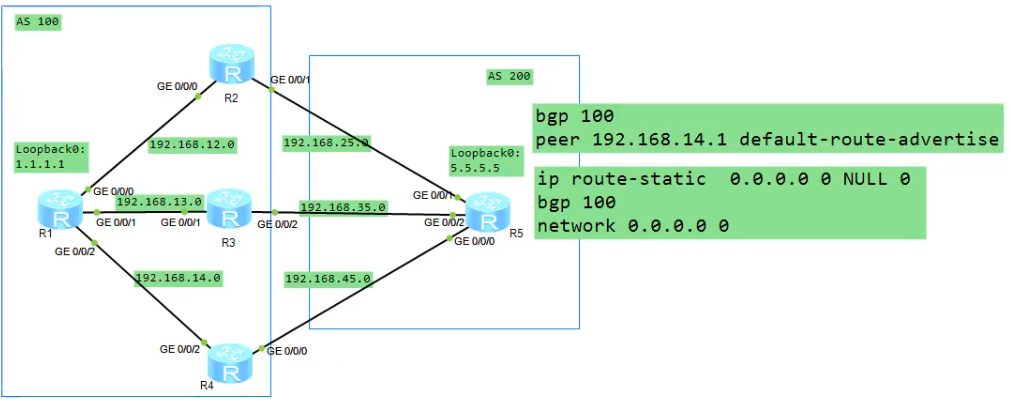
这个环境是直接用物理接口建立IBGP邻居。主要是为了说缺省路由有这么几种方式
R1
bgp 100
peer 192.168.12.2 as-n 100
peer 192.168.13.3 as-n 100
peer 192.168.14.4 as-n 100
net 1.1.1.0 255.255.255.0
R2
bgp 100
router-id 2.2.2.2
peer 192.168.12.1 as-n 100
peer 192.168.12.1 next-hop-local
peer 192.168.25.5 as-n 200
R3
bgp 100
router-id 3.3.3.3
peer 192.168.13.1 as-n 100
peer 192.168.13.1 next-hop-local
peer 192.168.35.5 as-n 200
R4
bgp 100
router-id 4.4.4.4
peer 192.168.14.1 as-n 100
peer 192.168.14.1 next-hop-local
peer 192.168.45.5 as-n 200
R5
bgp 200
router-id 5.5.5.5
peer 192.168.25.2 as-n 100
peer 192.168.35.3 as-n 100
peer 192.168.45.4 as-n 100
net 5.5.5.0 255.255.255.0
让R1收不到R5的环回口。为了验证缺省路由

这个配置就是告诉R2R3R4,你们不要把我5.5.5.5的条目告诉其他设备。
第一种方式(比较好)
[R4]bgp 100
[R4-bgp]peer 192.168.14.1 default-route-advertise
发一条缺省路由给R1
第二种方式
[R3]ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0 NULL 0
[R3]bgp 100
net 0.0.0.0 0 要宣告前必须存在路由条目
就可以下放到整个AS
第三种方式
[R1]ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0 192.168.12.2
最后在R1上dis ip routing-table
审核编辑:黄飞
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !
